Discovering How Our Brain Works
1. The Brain
– The brain is like a supercomputer inside our heads, and it’s the most complex part of our body.
It controls everything we do, from breathing to thinking. Picture it as a busy city, with billions of tiny workers called neurons constantly communicating with each other. These workers help us learn new things, feel emotions, and remember special moments. Our brain even helps us make decisions, like what to eat or which game to play. It’s amazing to think that this small, three-pound organ is responsible for everything we experience in life!
-Controller of bodily functions, thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
Think of your brain as the boss of your body. It’s in charge of everything! From making your heart beat to helping you feel happy or sad, your brain controls it all. It’s like a superhero, managing everything you do, from walking and talking to feeling emotions. Without your brain, you wouldn’t be able to do anything at all! So, you can see, your brain is super important!
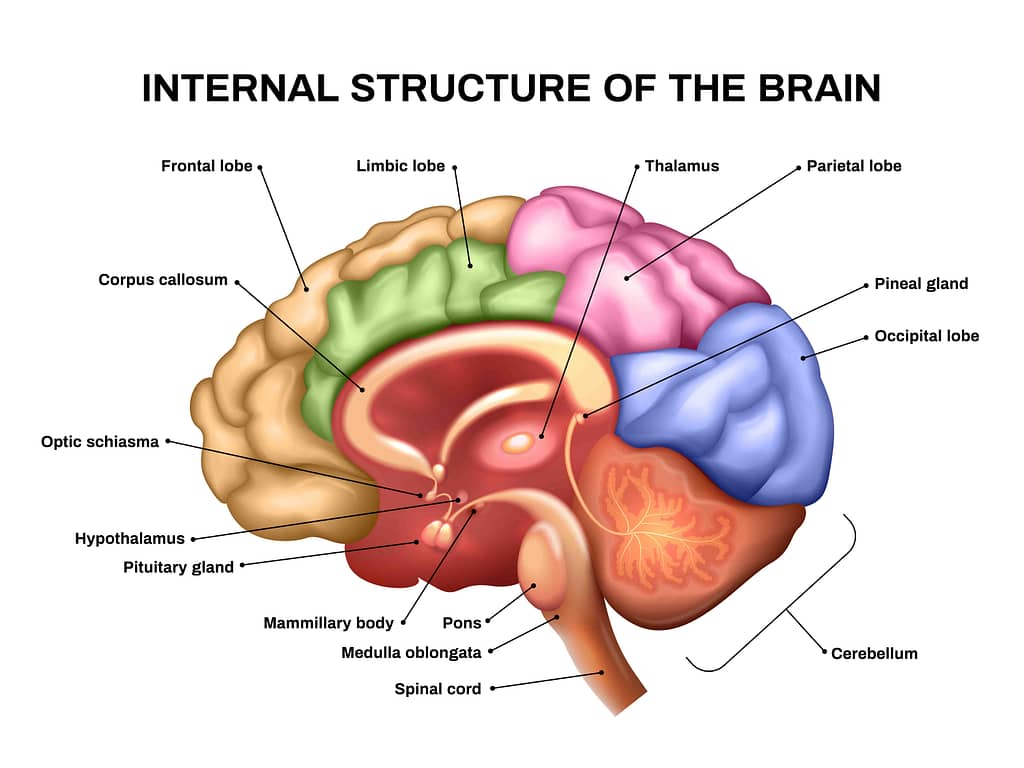
2. Brain Structure
– Basic structure of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and brainstem.
Your brain has different parts, like sections of a house. The biggest part on top is called the cerebral cortex. It helps you think and learn new things. Then, there’s the cerebellum, which is like a control center for your movements, such as walking or playing sports. The brainstem, which is located at the base and aids in breathing and heartbeat, is the last structure. Each part has its own job, like pieces of a puzzle, working together to keep you going strong!
– Functions associated with each major part of the brain.
| Cerebral Cortex | Cerebellum | Brainstem |
| Problem-solving | Walking and running | Breathing |
| Making decisions | Riding a bike | Heartbeat |
| Remembering things | Playing sports | Swallowing |
| Feeling emotions | Keeping your balance so you don’t fall over | Digestion |
| Understanding language | Sleeping and waking up | |
| Seeing and hearing things |
Your brain’s many functional regions work together to support every aspect of daily life, from thinking and movement to maintaining your health and survival!
3. Neurons and Synapses
– Neurons as the building blocks of the brain.
Neurons are like the little workers in your brain. They send messages to each other to help your brain and body do all kind of things, like thinking, moving, and feeling. Without neurons, your brain wouldn’t know what to do! They’re like the busy bees making everything happen up there.
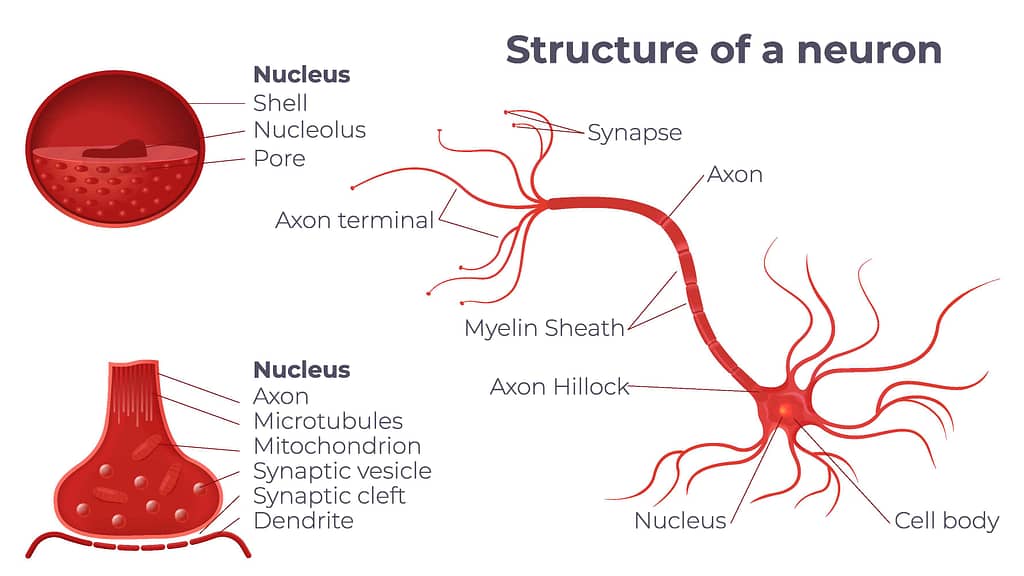
– How neurons communicate through synapses and neurotransmitters.
Neurons are like friends chatting with each other. Instead of talking, they use tiny gaps called synapses. When one neuron wants to tell another something, it sends a message with special chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals jump across the gap and deliver the message. Then, the next neuron decides what to do with the message—like passing it on or ignoring it. This quick talk between neurons helps your brain work smoothly, like a team!
– Role of synapses in learning and memory.
Synapses are like tiny switches in your brain that help you learn and remember. When you learn something new, these switches get stronger, like turning up the volume. Later, when you want to remember what you learned, these strong switches make it easier for your brain to find the right information. So, synapses are like little boosters that help your brain remember things better!
4. Brain Plasticity
– Brain plasticity and its significance in learning, memory, and recovery from injury.
Brain plasticity means your brain can change and learn new things. It’s like how your muscles get stronger when you exercise. When you learn or practice something, your brain makes new connections. This helps you remember things better.
If you get hurt, your brain can sometimes find new ways to do things. It’s like finding a different route when your usual road is blocked.
So, brain plasticity helps you learn, remember, and recover from injuries by letting your brain adapt and change. It’s like your brain’s superpower!
– Examples of brain plasticity, such as the brain’s ability to reorganize after trauma or during skill acquisition.
Recovery from Injury – If one part of your brain gets hurt, another part can sometimes learn to do its job instead.
Learning Skills – When you practice something new, your brain changes to get better at it. It’s like exercising your brain!
Vision Problems – If your eyes don’t work well, your brain might use other senses, like hearing or touch, to make up for it.
Feeling Missing Limbs – Even if you lose a limb, your brain might still think it’s there. It seems as though your mind is deceiving you!
These illustrations highlight how the brain is incredibly adept at adapting to changing circumstances and errors.
5. Sensory Processing
– How Brain processes sensory information from the environment.
Your brain uses your senses—like seeing, hearing, touching, tasting, and smelling—to understand the world around you:
1. Vision – Your eyes see things, and your brain turns that into pictures.
2. Hearing – Your ears hear sounds, and your brain recognizes what they are.
3. Touch – Your skin feels things, and your brain knows if they’re hot, cold, or painful.
4. Taste – Your tongue tastes flavors, and your brain tells you if something is sweet, sour, salty, or bitter.
5. Smell – Your nose smells scents, and your brain identifies them.

These illustrations highlight how the brain is incredibly adept at adapting to changing circumstances and errors.
– Different sensory modalities (vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell) and their corresponding brain regions.
1. Vision (Seeing) – Your eyes see things, and your brain understands them in the back part of your brain.
2. Hearing (Hearing) – Your ears hear sounds, and your brain processes them in the side part of your brain.
3. Touch (Feeling) – Your skin feels things, and your brain figures them out in the top part of your brain.
4. Taste (Tasting) – Your tongue tastes flavors, and your brain recognizes them in the front part of your brain.
5. Smell (Smelling) – Your nose smells scents, and your brain identifies them in the bottom part of your brain.
Each part of your brain has a special job for making sense of what your senses tell you. It’s like having different teams in your brain, each working on a different sense!
6. Emotional Regulation
– The brain regulates emotions and stress responses.
Your brain handles your feelings and reactions to stress:
1. Emotions – Your brain’s emotion center, the limbic system, makes you feel happy, sad, or scared when things happen.
2. Stress Responses – Another part of your brain, called the amygdala, acts like an alarm when you’re stressed.

– It tells your body to get ready for action, like making your heart beat faster and your muscles tense up.
So, your brain helps you understand your feelings and react to stress. It’s like your built-in guide for handling tough times!
– The role of limbic system, particularly the amygdala and hippocampus, in emotional processing and memory
1. Limbic System – It’s like your brain’s emotion and memory center.
– It helps you feel things and remember them.
2. Amygdala – This is your brain’s alarm button.
– It helps you react to scary or important stuff.
3. Hippocampus – This is your brain’s memory keeper.
– It helps you remember things, especially those linked to emotions.
So, the limbic system, including the amygdala and hippocampus, helps you feel emotions and remember things. It’s like your brain’s emotional memory bank!
7. Motor Control
– How brain controls voluntary and involuntary movements.
1. Voluntary Movements – These are movements you do on purpose, like raising your hand.
– Your brain’s motor cortex controls them.
2. Involuntary Movements – These are movements that happen automatically, like breathing.
– Your brainstem and cerebellum handle them.
Your brain takes care of both kinds of movements, whether you’re doing something on purpose or it’s happening without you even thinking about it. It’s like your brain has different teams for different types of movements, making sure everything runs smoothly!
– The motor cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum in motor coordination and learning.
1. Motor Cortex – This part plans and does movements you decide to make, like waving your hand.
2. Basal Ganglia – It helps you do movements smoothly, like drawing a straight line or catching a ball.
3. Cerebellum – It’s like your balance and coordination coach, making sure you move without wobbling.
So, the motor cortex plans, the basal ganglia smooths, and the cerebellum balances—helping you move and learn new skills with ease!
8. Language and Communication

– The brain regions involved in language processing, such as Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area.
1. Broca’s Area
– This helps you talk.
– It puts words together into sentences.
2. Wernicke’s Area
– This helps you understand.
– It makes sense of words and sentences.
So, Broca helps you talk, and Wernicke helps you understand—like two friends working together to make communication happen!
– How brain comprehends and produces speech.
1. Understanding Speech – When someone talks, your brain figures out what they’re saying using a special area called Wernicke’s area.
2. Producing Speech – When you want to talk, another part of your brain called Broca’s area helps you turn your thoughts into words.
So, Wernicke’s area helps you understand speech, and Broca’s area helps you speak. They work together like a team to help you communicate with others!
9. Consciousness and Decision Making
– The concept of consciousness and how the brain generates subjective experiences.
1. Consciousness
– This is like being awake and aware of the world around you.
– It’s what makes you feel like “you” and experience life every day.
2. Brain and Your Feelings
– Your brain is like a control center in your head.
– It creates your feelings and experiences based on what’s happening, like a movie director making a film.
So, consciousness is being awake and aware, and your brain is like the director of the movie of your life, creating all your feelings and experiences.
– The role of different brain regions in decision-making processes and free will.
1.Decision-Making
– When you make decisions, different parts of your brain work together.
– Your “thinking” part of the brain, called the prefrontal cortex, helps you choose between options.
2. Free Will
– Free will is like your ability to choose what you want to do.
– It’s based on your thoughts, feelings, and experiences, which all come from your brain.
So, your brain’s prefrontal cortex helps you decide, and free will is your ability to choose freely. It’s like having a smart friend in your head helping you pick what’s best for you!
10. Disorders and Diseases
– common brain disorders and diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, schizophrenia, and depression.
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
– This affects memory and thinking skills as you get older.
– It can make it hard to remember things, think clearly, and do everyday tasks.
2. Parkinson’s Disease
– This affects movement, causing tremors, stiffness, and slowness.
– It can also cause problems with balance and coordination.
3. Schizophrenia
– This affects how you think, feel, and behave.
– It can cause hallucinations, delusions, and trouble concentrating.
4. Depression
– This affects mood and emotions, causing persistent sadness and loss of interest.
– It can also lead to changes in sleep, appetite, and energy levels.
– Research and treatments for these conditions.
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
– Scientists are trying to slow it down by targeting bad proteins in the brain.
– Treatments focus on managing symptoms and making life better.
2. Parkinson’s Disease
– Researchers are working on better meds and treatments to control symptoms.
– Surgery like deep brain stimulation helps some people.
3. Schizophrenia
– Scientists are finding meds with fewer side effects.
– Therapy and support groups help a lot too.
4. Depression
– New meds and therapies are being studied to help people feel better.
– Counseling and support are important for managing it.
They’re still figuring out better ways to help, but treatments and support are making a difference!
11. Future Directions in Neuroscience
– Technologies and research techniques in neuroscience, such as optogenetics, brain-computer interfaces, and neuroimaging.
1. Optogenetics – Using light to control brain cells and understand how they work.
2. Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) – Letting people control computers or prosthetics with their thoughts.
3. Neuroimaging – Taking pictures of the brain to see how it works using techniques like MRI and CT scans.
– Speculate on potential breakthroughs and their implications for understanding the brain.
1. Brain Disorders – Breakthroughs could mean better treatments or even cures for conditions like Alzheimer’s and depression.
2. Brain-Computer Interfaces – Advances might let people control things using just their thoughts, helping those with disabilities.
3. Learning About the Brain – Discoveries could teach us how the brain works, how we learn, and why we feel and act the way we do.
4. Personalized Treatments – Breakthroughs could lead to treatments tailored to each person’s unique brain, making them more effective.

